In today’s digital world, data has become one of the most valuable resources. Photos, documents, websites, customer databases, accounting records — all of this is stored electronically and requires protection. When it comes to data security, two terms are mentioned most often: backup and replication. For many users, they sound similar because both involve copying information. However, in practice these are different approaches that solve different problems. Understanding this difference is important not only for system administrators, but also for website owners, businesses, and anyone who stores important data.
What a backup is and why it is needed
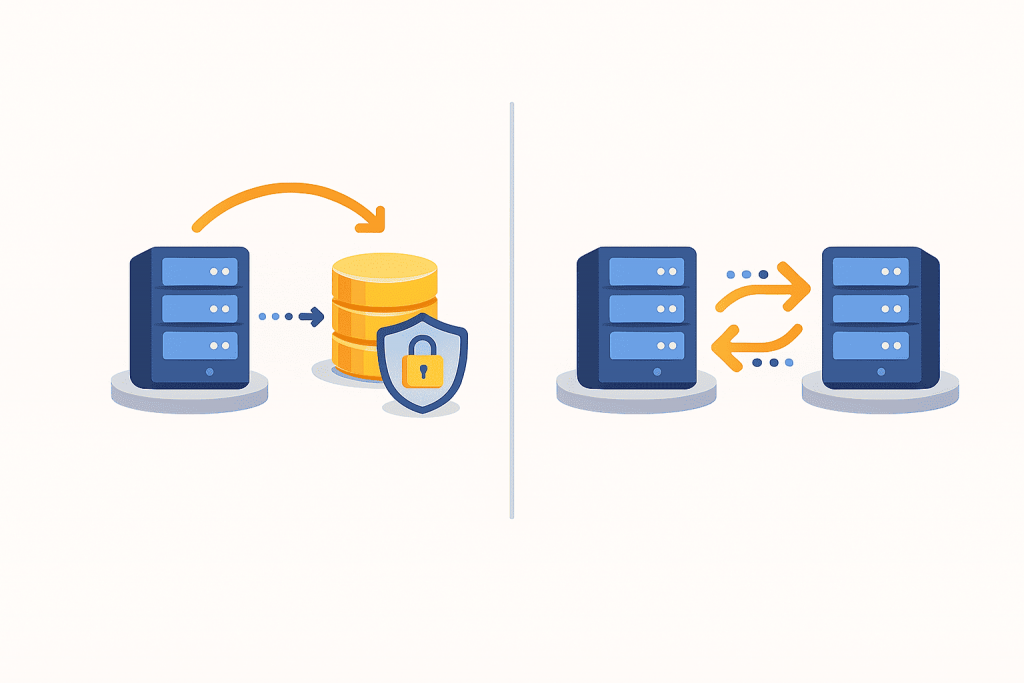
A backup, or backup copy, is the creation of a copy of data for later recovery in case of loss. Simply put, a backup is a “spare version” of your files that is stored separately from the main system. If a server fails, a website breaks after an update, files are deleted by mistake, or data is damaged by a virus, a backup is what allows everything to be restored to a working state.
As a rule, backups are created on a schedule — once a day, several times a day, or once a week, depending on how important the data is. A backup captures the state of the system at a specific point in time. If a problem occurs today, you can roll back to yesterday’s version or even an earlier one. This is the key feature of backup systems — the ability to go back in time and restore data as it existed before a failure.
What replication is and how it works
Replication is the process of continuously or almost instantly copying data from one location to another. Most often, it is used to maintain an up-to-date copy of a system on another server. When data changes on the primary server, those changes are immediately transferred to the secondary one. As a result, both systems contain the same synchronized information.
The main purpose of replication is to ensure uninterrupted operation of services. If the primary server stops working due to hardware failure or data center issues, it is possible to quickly switch to the replica and minimize downtime. For users, this looks as if the service hardly stopped at all. That is why replication is often used in large projects, online stores, financial systems, and services where every minute of downtime means lost revenue.
The key difference between backup and replication
Despite their apparent similarity, backup and replication play fundamentally different roles. A backup stores the history of data states, while replication maintains a current copy of the data. Using a simple analogy, a backup is like an archive of photos taken on different dates, whereas replication is a mirror that always shows the current state.
This means that replication does not protect against logical errors. If a file is accidentally deleted or a database is corrupted, these changes will be instantly copied to the replica as well. In such a situation, only a backup created before the mistake can save the data. That is why replication cannot replace backups, even if it seems like a more advanced and modern solution.
When a backup is needed
Backup is necessary whenever there is a risk of data loss. It is especially important for websites that are regularly updated, for servers with customer databases, financial data, or important documentation. Backups help in cases of human error, failed software updates, file system issues, or malware infections.
For most small projects and personal websites, a reliable backup already provides a sufficient level of protection. The key point is that backup copies should be stored separately from the main server and regularly tested for successful recovery.
When replication is essential
Replication becomes relevant when uninterrupted operation is the top priority. If a service cannot afford long downtime, a backup alone is not enough. Restoring from a backup takes time, while a replica allows work to continue almost instantly.
Such solutions are usually used in high-load projects where every minute of downtime is critical. However, even in these cases, replication is always complemented by backups rather than replacing them.
Why the best option is to combine both approaches
Backup and replication are not competitors, but complementary tools. Replication provides stability and availability of a service here and now, while backups ensure the ability to restore data in case of any errors or disasters. Together, they form a comprehensive data protection strategy that covers most risks.
Understanding the difference between these approaches helps to choose the right data storage strategy and avoid relying on false assumptions. True data security does not start with fashionable terms, but with informed decisions and the right tools.

Leave a Reply