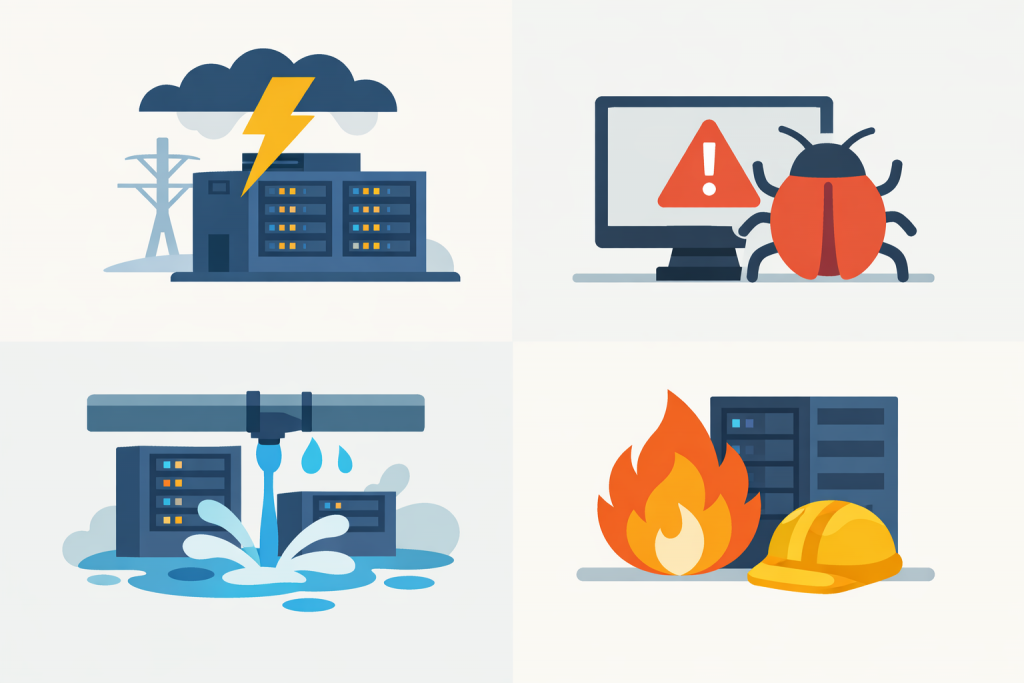
From the outside, a data center (DC) looks like an unshakable fortress: autonomous power supply, sealed halls, multi-level monitoring. We are used to clouds, banking and streaming simply working 24/7. But behind this stability stands a complex engineering ecosystem where the failure of a single node can trigger a cascade reaction that automation does not always manage to intercept in time.