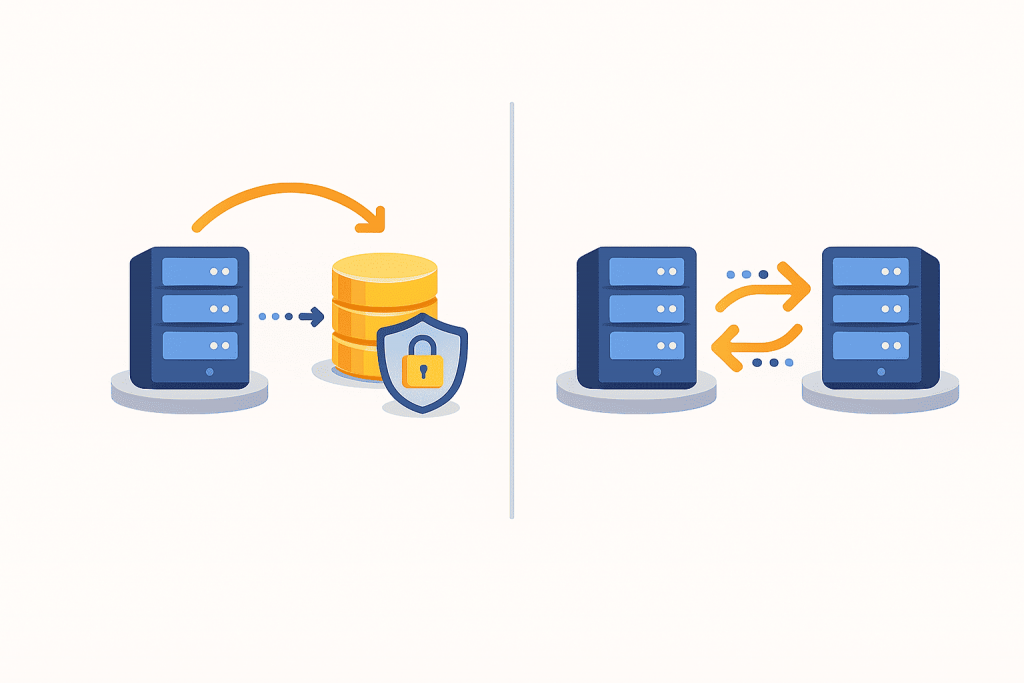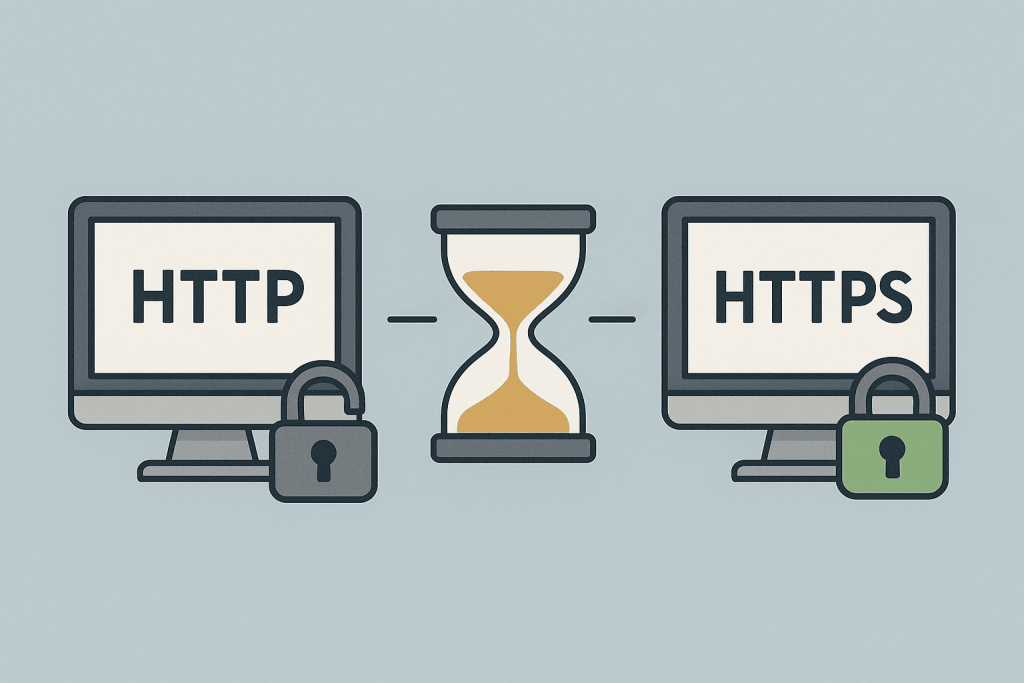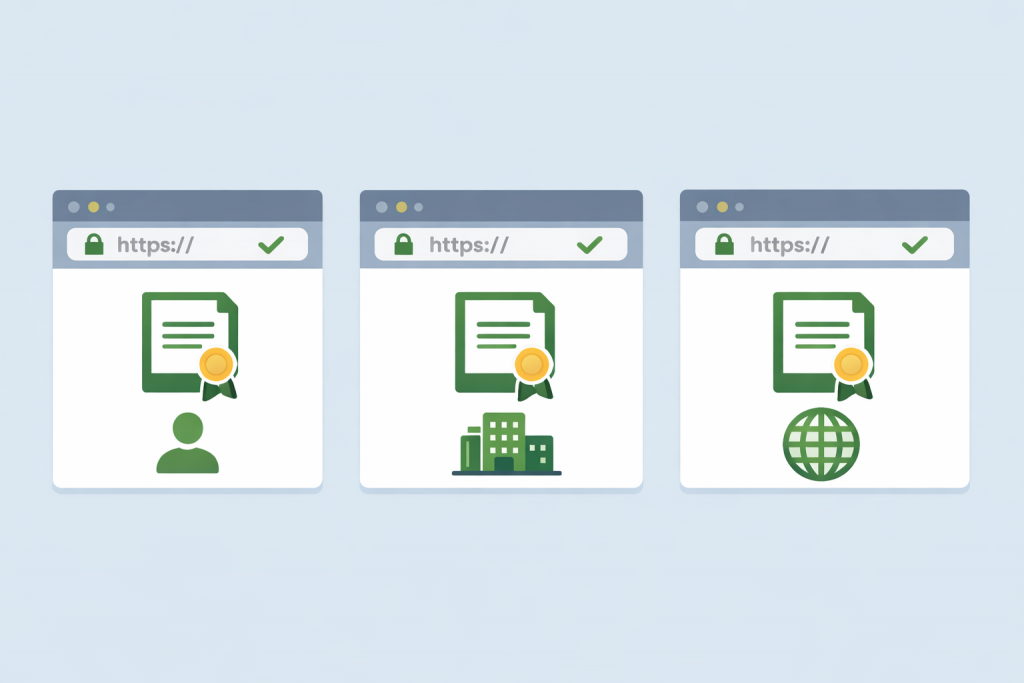
An SSL certificate is a digital document that confirms the authenticity of a website and ensures a secure connection between the user’s browser and the server. Thanks to SSL, the data that a visitor enters on a website is transmitted in encrypted form and cannot be read by third parties. This applies to passwords, contact forms, payment information, and any personal data. For users, the presence of SSL is usually visible as a padlock icon in the browser’s address bar, while for a website it is a mandatory condition for trust, correct operation of many services, and proper ranking in search engines.