API stands for Application Programming Interface, which is a software interface for interaction between different systems. Simply put, an API is a set of clear rules that allow one program to communicate with another, send a request, and receive a response. End users usually do not see APIs and rarely think about their existence, yet they use them constantly. Logging in with Google, paying by card on a website, displaying the weather, exchange rates, or delivery status — all of this works thanks to APIs.
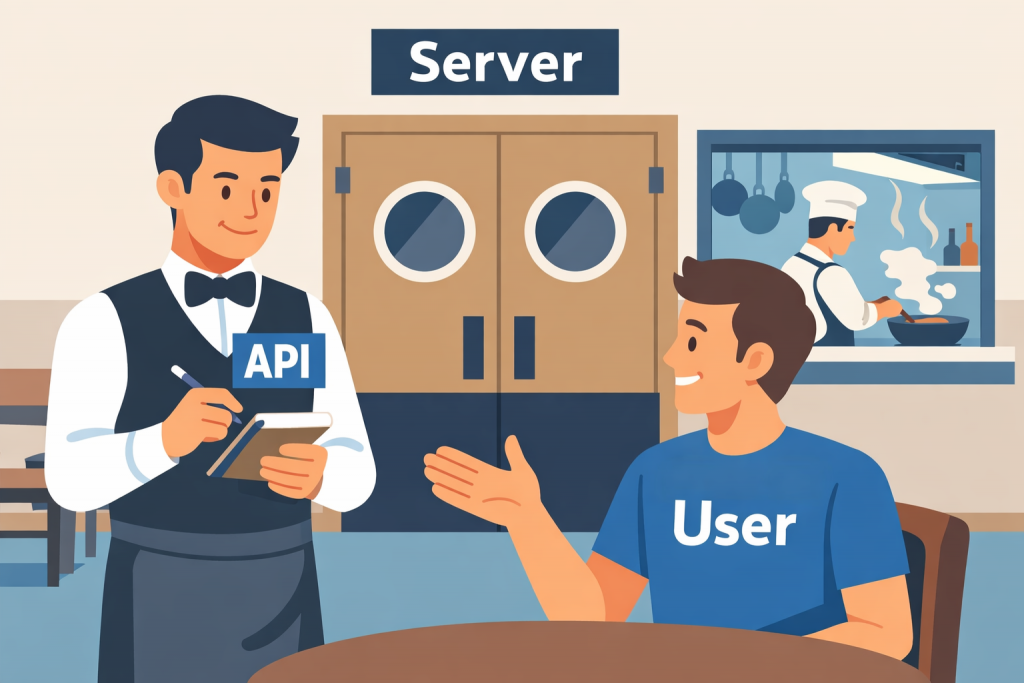
An API can be compared to a waiter in a restaurant. You do not go into the kitchen and explain to the chef how to prepare a dish. You simply place an order, and the waiter passes it on and returns with the finished result. The same applies to an API: it receives a request, passes it to the system, and returns a response in a clear format.
Why APIs Exist in Almost Every Modern Service
Modern services rarely operate in isolation. They interact with payment systems, delivery services, CRM platforms, mobile applications, analytics tools, and external platforms. APIs allow these systems to exchange data quickly, securely, and without manual intervention.
Thanks to APIs, companies can focus on developing their core product rather than building auxiliary services. An online store connects payments via a payment provider’s API, a delivery service receives order addresses through an API, and a mobile application communicates with the server using the same mechanisms. That is why APIs have become the foundation of most online products today.
How APIs Work in Practice
When one program needs data or an action to be performed, it sends a request to an API. The request specifies what is needed, for example, retrieving a list of products, creating an order, or checking the status of a payment. The server receives this request, processes it, and returns a response.
All this logic usually runs on a VPS or a dedicated server. The server ensures constant API availability, request processing, and data protection. If the server is unstable or cannot handle the load, the API starts responding slowly or with errors, which users immediately notice. Therefore, for APIs, not only the software part matters, but also a reliable server infrastructure.
What API Keys Are and Why APIs Do Not Work Without Them
Most APIs are not open to everyone. To let the server understand who is sending a request and whether they are allowed to use the service, API keys are used. An API key is a unique digital identifier that is sent along with every API request.
An API key can be compared to an electronic access pass. When a service issues a key, it effectively identifies the client and defines what actions are allowed. A server running on a VPS checks this key before processing a request. If the key is valid, the request is executed; if not, the server returns an error.
Keys make it possible to control access to an API, limit the number of requests, track activity, and protect the system from abuse. For example, if an API is used to work with personal data or financial transactions, operating without API keys and access checks would simply be unsafe.
Why Businesses Need APIs and API Keys
For businesses, APIs are not just a technical tool, but a way to automate processes and scale operations. Through APIs, orders can be transferred automatically between systems, databases can be synchronized, services can be managed, and up-to-date information can be obtained in real time. API keys ensure control and security in this interaction.
This is especially important for online projects that operate continuously and serve a large number of users. Hosting an API on a VPS allows flexible resource management, quick response to growing loads, and stable service operation without interruptions.
Why Users Do Not See APIs but Fully Depend on Them
An ordinary user does not enter API keys or send requests manually, but the speed of a website, the functionality of a mobile application, and the accuracy of data updates all depend on APIs. When an API is stable and well configured, the service feels simple and convenient. When problems occur with the server or API access, users immediately encounter errors and delays.
That is why companies pay so much attention to API quality, key security, and server infrastructure stability. A reliable VPS or dedicated server in this case is not a luxury, but a necessity.
API as the Foundation of the Modern Digital World
An API is an invisible mechanism that connects services, applications, and platforms. It allows systems to interact, automate processes, and develop products faster. API keys play the role of control and security, without which modern online services simply could not exist.
Understanding what an API is and how it works helps better explain why modern services look and function the way they do. It is not just a technical term, but the foundation of digital infrastructure that ensures the convenience and stability of online services every day.

Leave a Reply