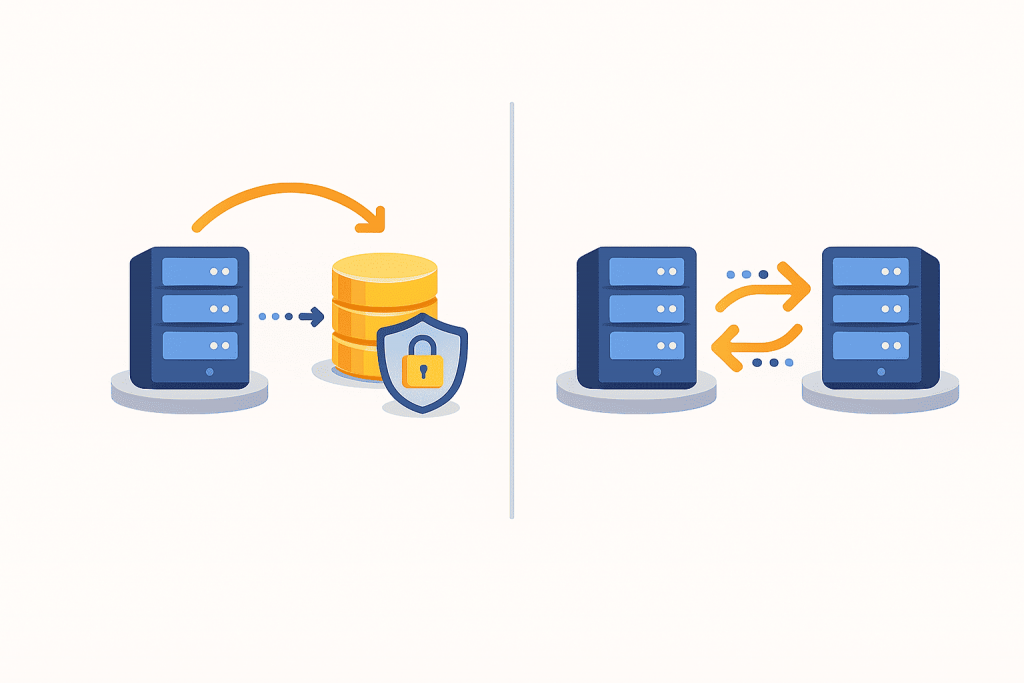
In today’s digital world, data has become one of the most valuable resources. Photos, documents, websites, customer databases, accounting records — all of this is stored electronically and requires protection. When it comes to data security, two terms are mentioned most often: backup and replication. For many users, they sound similar because both involve copying information. However, in practice these are different approaches that solve different problems. Understanding this difference is important not only for system administrators, but also for website owners, businesses, and anyone who stores important data.